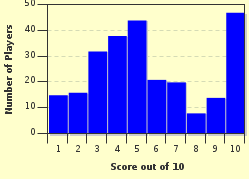
Quiz Answer Key and Fun Facts
1. A document at the heart of the English system of government, the Magna Carta, was established in what year?
2. Off with his head! What year was the execution warrant for Charles I of England issued?
3. In what year was the Treaty of Utrecht signed?
4. Among the first documents governing settlers in the colonies, The Mayflower Compact was established when?
5. The Monroe Doctrine was written in what year?
6. The Treaty of Fontainbleau was signed in what year?
7. The Decembrist Manifesto was set forth in which year?
8. What year was the Treaty of Versailles signed?
9. What year was the Atlantic Charter issued?
10. Pope Boniface VIII issued his papal bull entitled "Unam Sanctam" in which of these years?
Source: Author
rockinryder
This quiz was reviewed by FunTrivia editor
bloomsby before going online.
Any errors found in FunTrivia content are routinely corrected through our feedback system.