What are the Names of these Constellations? Quiz
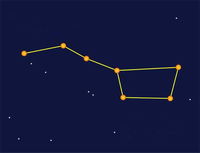
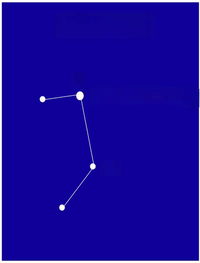
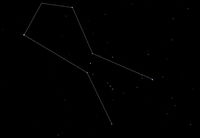
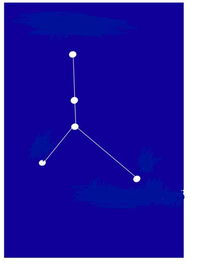
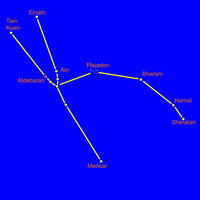
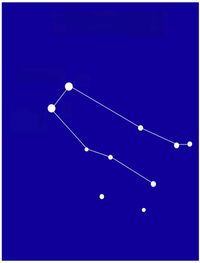
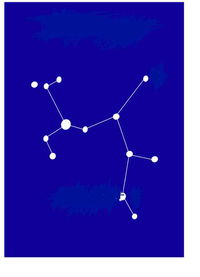
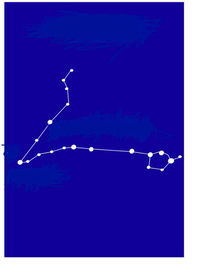
All you have to do is match the name of the constellations or asterisms to the photos. Some of the photos do not show the whole constellation, just enough to enable you to identify it. Good luck and have fun. Digby
by Lord_Digby.
Estimated time: 3 mins.
- Home
- »
- Quizzes
- »
- Science Trivia
- »
- Astronomy
- »
- Stars